Renewable Energy
The Renewable Energy Strategy in the City’s Climate Action Plan (CAP) aims to increase supply and access to renewable energy for existing and new residences, commercial properties, and municipal facilities. Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar and wind will reduce pollution, including greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
To accomplish this, the City’s CAP calls for the launch of a Community Choice Energy (CCE) program, the installation of solar panels on homes and businesses, and the addition of solar panels on municipal facilities, among other initiatives. Implementation of these measures is estimated to reduce the City’s GHG emissions by 434 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (MTCO2e) by 2020 and 20,935 MTCO2e by 2030.
Explore the sections below to see what the City is doing to achieve these goals.
RE-1: Establish a Community Choice Energy Program
100% Renewable Electricity by 2030
One of the key goals of the City’s Climate Action Plan (CAP) was to launch a Community Choice Energy (CCE) program that serves 100% renewable electricity to customers by 2030. CCE programs are not-for-profit, locally controlled energy agencies that purchase clean electrical power on behalf of residents and businesses.
In 2019, after the completion of a Technical Feasibility Study, the City formed a CCE Joint Powers Authority along with the cities of San Diego, Chula Vista, La Mesa, and Imperial Beach. Operating as San Diego Community Power (SDCP), the new agency began serving power to customers on March 1, 2021. Service was rolled out in the following phases:
- Phase 1: March 1, 2021 - Municipal Customers
- Phase 2: June 1, 2021 - Commercial Customers
- Phase 3: April 1, 2022 - Residential and Solar Customers (Net Energy Metering)
As part of this roll-out, Encinitas City Council voted to establish SDCP’s premium product, Power100, as the default electricity choice for all customers within the City of Encinitas. Power100 provides 100% renewable electricity to customers at a cost that is only marginally greater than San Diego Gas and Electric’s (SDGE) current rates, 1 to 3% greater depending on the rate class. This action enables the City to achieve its 100% renewable electricity goal well in advance of the 2030 target date.
UNIT | A kilowatt is a measure of power, or how fast something generates or uses energy. The capacity of a solar photovolatic (PV) system to generate energy is measured in watts. Solar PV systems installed on single family homes typically range in size from 5 kW to 20 kW. One kilowatt equals 1,000 watts. | kWKilowatt |
A kilowatt is a measure of power, or how fast something generates or uses energy. The capacity of a solar photovolatic (PV) system to generate energy is measured in watts. Solar PV systems installed on single family homes typically range in size from 5 kW to 20 kW. One kilowatt equals 1,000 watts. | kWKilowatt |
Last updated March 4, 2024
MRE-1: Supply Municipal Facilities with Renewable Energy
Municipal Facilities with On-Site Renewable Energy
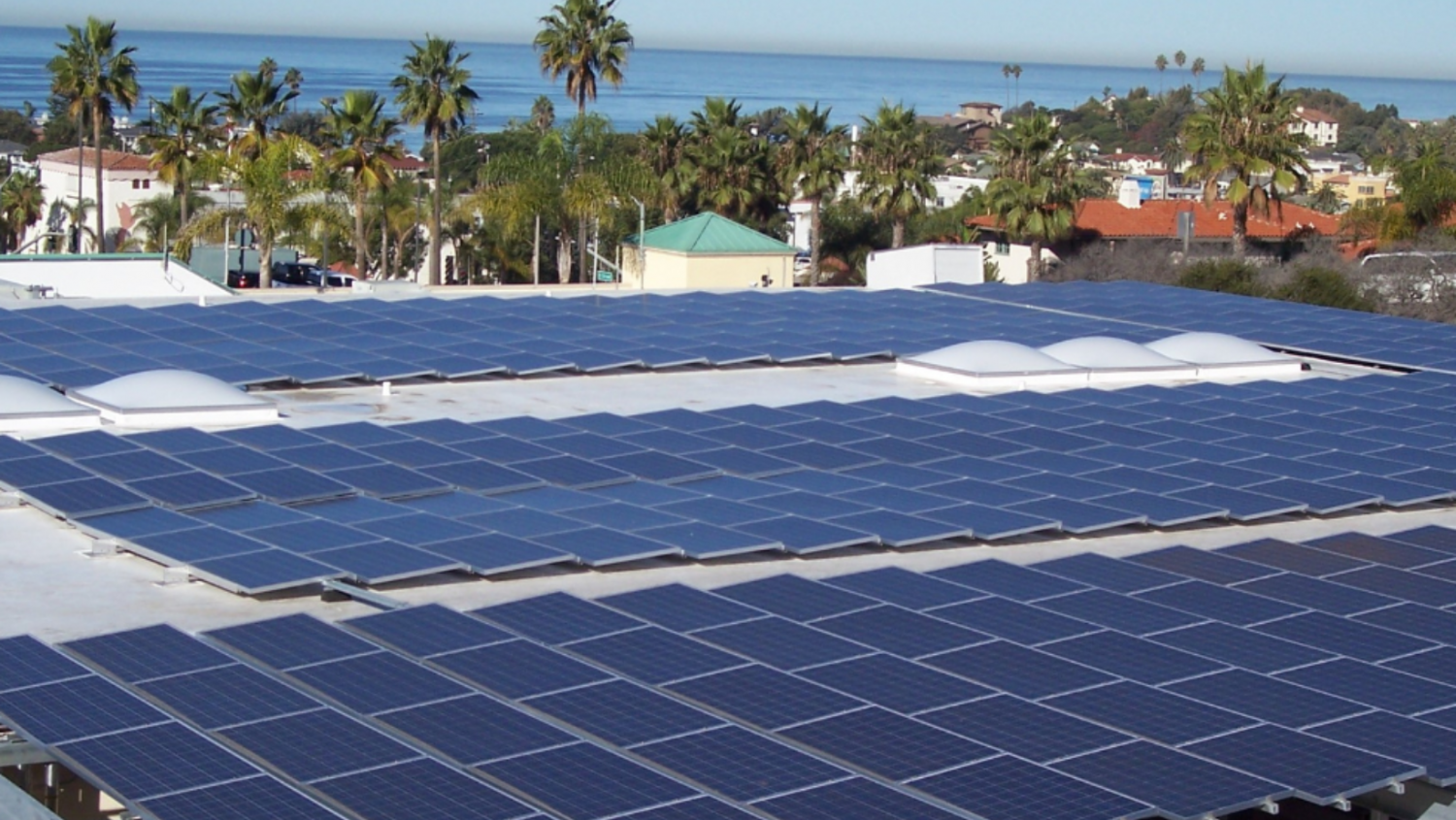
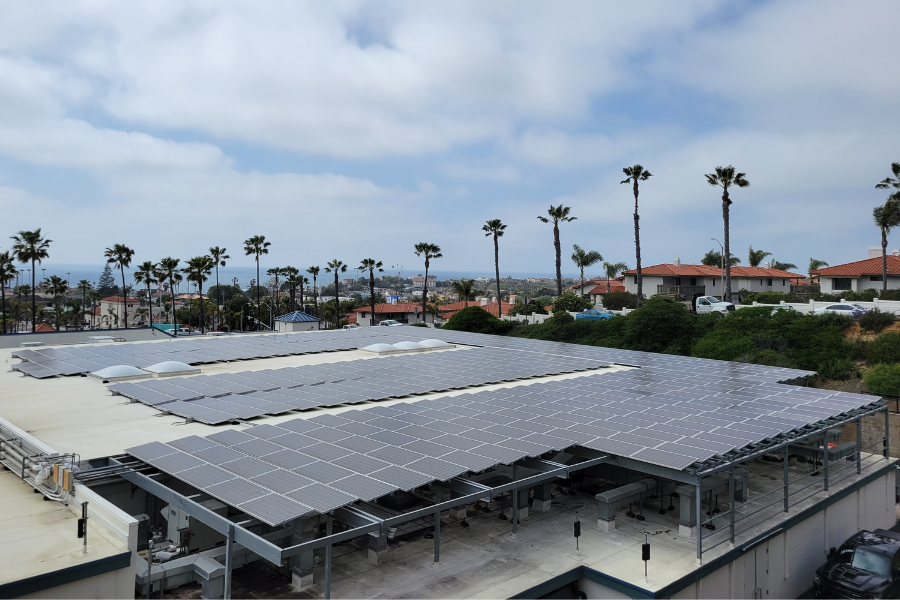
CAP measure MRE-1 set an ambitious goal of supplying all municipal facilities with enough onsite renewable energy to achieve “Net Zero Electricity.” This means that municipal buildings would generate as much electricity as they consume. The CAP goal is to supply 50 percent of its municipal energy needs from renewable sources by 2020 and 100 percent by 2030.
In 2008, the City installed a 96-kilowatt (kW) solar PV system at City Hall. The system generates approximately 150 megawatt hours (MWh) of electricity each year, which is equivalent to about 7 percent of the City’s total municipal building electricity use, annually.
In 2019, the City acquired an energy consultant to design and install solar PV systems for the Community and Senior Center, the Public Works building on Calle Magdalena, the Encinitas Public Library, and add more solar panels on City Hall as part of a “paid-through-savings” program. In 2020, this project was put on hold due to COVID-19 and other competing financing needs. This project will be revisited as part of a future City budget cycle. In the meantime, as of 2021, all City facilities are served with 100 percent renewable electricity provided by San Diego Community Power.
Last updated July 10, 2024
Homes and Businesses
How You Can Help

Last updated August 30, 2022