On November 18, 2020, City Council adopted an updated Climate Action Plan (CAP) which included a recalculation of anticipated future greenhouse gas emissions, updates to many CAP measures, and a commitment to a more aggressive greenhouse gas reduction target, yet again, establishing the City of Encinitas as a leader in climate action.
A Quick Refresher:
You may recall, in 2018, City Council adopted an updated Climate Action Plan (CAP) which included detailed numeric greenhouse gas reduction targets with specific implementation goals and actions. By adopting such an express commitment, the City established a new standard in climate action, one that many other cities in the region now seek to model. Following CAP adoption, in March 2019, the city adopted an updated Housing Element, adding 1,504 housing units on 19 future development sites. The Housing Element’s Environmental Impact Report determined that the additional housing may increase citywide greenhouse gas emissions and therefore required that the City mitigate for the these impacts by updating the City’s CAP.
Where We Are Now:
In 2020, City staff worked with climate planning consultants and SANDAG to incorporate the additional housing sites into the City’s CAP. This involved reassessing land use and transportation impacts on greenhouse gas emissions and incorporating newly established State and Federal legislation enacted since the adoption of the CAP in 2018. Recent insights based on the City’s latest CAP implementation also helped guide the updates. The updated CAP was approved unanimously by City Council on November 18, 2020. The following blog post describes the major updates that were made to the document.
CAP Updates:
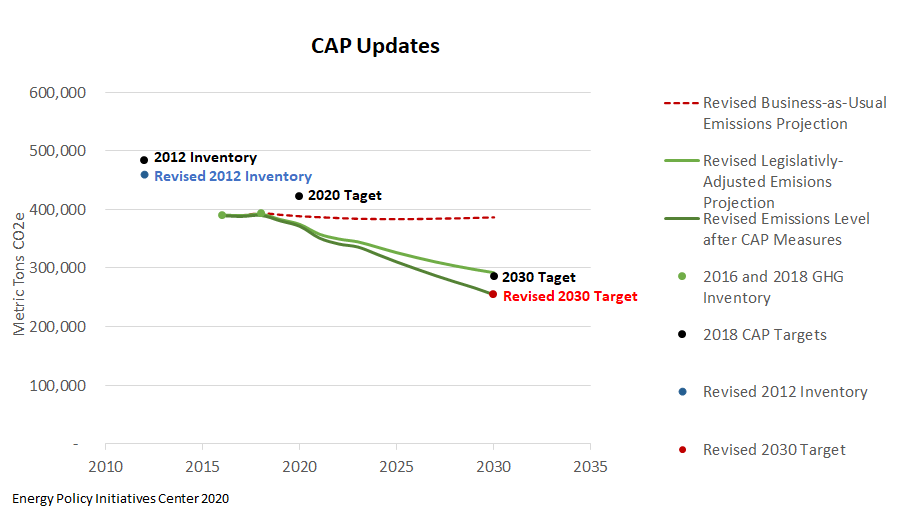
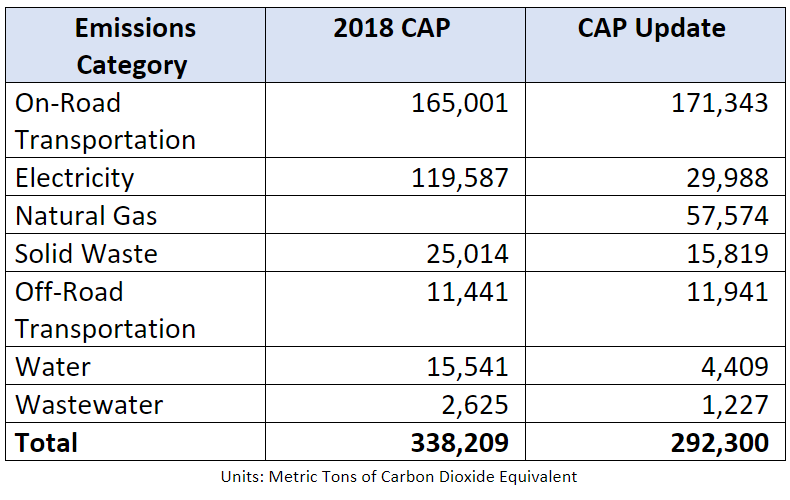
Since the 2018 CAP update, various regional and statewide climate datasets were updated with more recent and accurate information. In particular, new information was available for California vehicle emissions, renewable energy on our local electrical grid, and regional recycling and waste disposal. Overall, this resulted in a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions in almost every category. This is great news!
As part of this latest CAP update, several improvements were made to the CAP Measures, the actions the City will take to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Multiple measures under the Building Efficiency strategy were revised to be more effective. According to updated CAP Measure BE-1, the City will develop a residential energy efficiency ordinance rather than an energy audit program. CAP Measure BE-2 originally addressed residential and commercial solar water heating, but will now focus on building decarbonization. Building decarbonization supports the use of electricity to power large appliances in buildings such as space heating and water heating. As the electrical grid becomes more renewable, this transition will facilitate reductions in carbon emissions from building activities. To support the aforementioned CAP measures, new supporting measures were developed, such as supporting state decarbonization legislation, and offering education and outreach on building electrification.
Measures under the CAP strategy, Clean and Efficient Transportation, were also updated to improve the scope and implementation of goals related to vehicle emissions. Formerly, CAP Measure CET-1 did not include numeric targets; now, with the completion of the Active Transportation Plan, numeric targets were able to be calculated and included based on the assumption that all bike and pedestrian infrastructure projects identified in the ATP would be completed by 2030. CAP Measure MCET-2, a new addition, will establish a municipal employee telecommute policy for the City, supporting emissions reductions through emerging trends in commuting. The CAP update also added new supporting measures to promote clean transportation, including installing more bike parking and other infrastructure enhancements to encourage alternate, low-carbon forms of transportation. The City will also initiate routine surveys of biking, walking, and transit ridership to ensure any adjustment in mode shifts due to new infrastructure can be detected. Completion of the Modal Alternatives Plan, another new supporting measure, will also further opportunities for biking and walking by developing concept plans for the high priority ATP projects.
Finally, and probably the most exciting update to report on, the 2030 GHG Reduction Target in the CAP was changed from 41% to 44% to align the new and modified CAP measures and anticipated reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, highlighting our city’s continued commitment to taking an strong stance on climate action.
With your support and participation, we look forward to continuing to move towards a more resilient and sustainable Encinitas.